Delivering Sustainable Manufacturing to the Automotive Industry: The Role of Large Format 3D Printing
Sustainability has become a significant driver of social and economic change globally, impacting industries across the board. However, achieving sustainability goals has often been sidelined by complexity and cost, particularly in sectors like automotive that prioritize efficiency and scale. Nevertheless, due to international standards and governmental policies, the automotive industry faces increasing pressure to reduce its environmental impact in vehicle production, supply chains, and manufacturing processes. Key issues include energy sources, alternative fuels, lightweight vehicle construction, and CO2 emissions reduction.
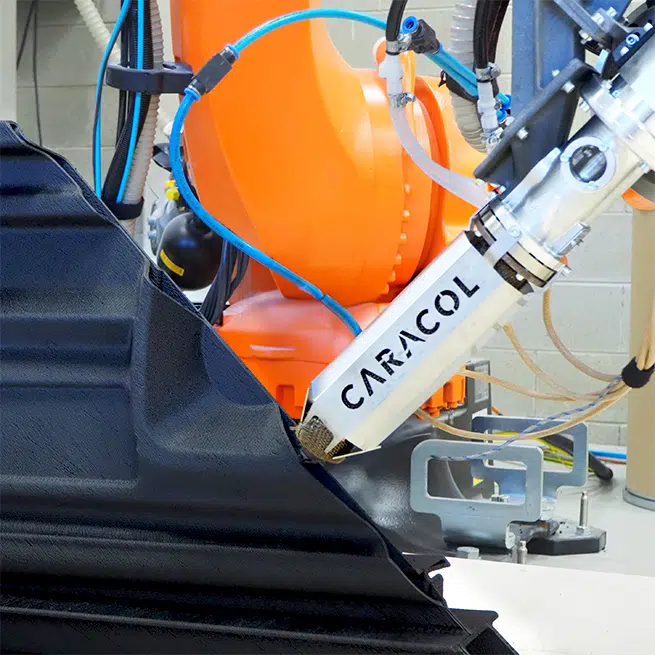
Recently, we explored the benefits of Large Format Additive Manufacturing in automotive applications. This article focuses on how large-scale 3D printing can introduce sustainable production practices, revolutionizing traditional manufacturing methods.
WHAT IS SUSTAINABILITY IN THE AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY
Achieving sustainability in the automotive industry involves balancing efficiencies, growth, and actions for environmental and social responsibility. It requires managing diverse stakeholder needs—from automakers and suppliers to policymakers and consumers—to drive meaningful change toward cleaner, safer, and more inclusive mobility. The path to sustainability involves key aspects:
- Environmental Impact Reduction: focuses on minimizing carbon emissions, air, water, and land pollution by using cleaner energy, lightweight materials for better fuel efficiency, and eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
- Resources Conservation: emphasizes efficient use of raw materials and energy through recycling, waste reduction, and promotion of renewable resources.
- Lifecycle Management: considers the entire vehicle lifecycle, including design, production, use, and disposal, by simplifying manufacturing processes, using durable materials, and implementing end-of-life recycling programs.
- Social Responsibility: includes fair labor practices, diversity, and community support achieved through ethical material sourcing, safe working conditions, and community engagement.
- Innovation and Technology: relies on continuous advancements like electric vehicles, autonomous driving technologies, and lightweight materials to enhance overall efficiency in the automotive industry.
HOW LARGE FORMAT 3D PRINTING IS FOSTERING SUSTAINABILITY IN THE AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY
Large Format Additive Manufacturing (LFAM) technologies, such as Caracol’s Heron AM robotic platforms, drive sustainability across various domains:
1. Resource Efficiency
LFAM helps optimize resource utilization. 3D printing traditionally builds components layer by layer, precisely adding material where needed – minimizing material waste, leading to significant resource savings. This is especially true on larger parts, where hundreds of kilograms of materials are needed. Also, energy needed for production is reduced, often thanks to shorter machine hours, and overall contributing to a more sustainable production cycle.
2. Optimized & Lightweight Design
LFAM enables the creation of lightweight yet robust parts, often also consolidating in a single part with no need for assemblies, as, by leveraging DfAM techniques it is possible to optimize design. Often materials can be replaced, leveraging advanced compounds like carbon fiber-filled thermoplastics or aluminum alloys. 3D printed components maintain structural integrity while being lighter, without compromising performance or safety, and sometimes improving aerodynamics and vehicle performance. Ultimately this allows to streamline the manufacturing process, and lightweight vehicles also consume less fuel and emit fewer greenhouse gases.
3. Customization
LFAM offers significant advantages in boosting customization and production efficiency for highly specialized car parts used in small series, racing, and supercar models. Its flexibility in design allows for intricate and tailored components that meet unique specifications without the constraints of traditional manufacturing processes. Therefore, automakers can rapidly prototype and produce custom parts, optimizing performance and aesthetics for specialized vehicles. Additionally, its process efficiency reduces production time and costs associated with tooling and setup, making it economically viable for small production runs of exclusive vehicles where customization is paramount. As a result, with large-scale 3D printing it’s possible to create high-performance, uniquely tailored vehicles that cater to niche markets and enthusiast demands.
4. Digital Local Production
LFAM allows to introduce production locally, at point of use of the parts, enabling automakers to establish smaller-scale manufacturing facilities closer to their assembly plants. This decentralization reduces transportation-related carbon emissions associated with global supply chains. Additionally, it promotes regional economic development by creating jobs and supporting local industries. By adopting a decentralized manufacturing model, with globally available digital inventories, automotive companies can respond more swiftly to market demands, reduce inventory, and minimize the environmental impact of transportation and logistics.
5. Lifecycle Sustainability
The sustainability benefits of LFAM extend beyond the manufacturing phase. Additive manufacturing enables the repair and refurbishment of components, producing on demand also out-of-stock or obsolete parts, extending their lifecycle and reducing the volume of discarded parts, as well as recycling materials from tooling used in manufacturing or of parts at the end of life. Furthermore, 3D printing facilitates on-demand production, reducing the need for excess inventory and eliminating overproduction.
In conclusion, large format 3D printing transforms the automotive industry as far as sustainability is concerned, by promoting resource efficiency, lightweight design, customization, localized production, and lifecycle sustainability. This technology enables automakers to reduce their environmental impact while advancing innovation and competitiveness, playing an increasingly pivotal role in fostering sustainability and driving the transition towards a greener future.